Grid
# Grid
Grid is a dataset PCF wrapper over Virtual Dataset. It allows you to use the same features that are available in the Virtual Dataset while enabling direct binding to a Subgrid or Homepage grid. This page only covers the differences between the Grid and Virtual Dataset controls. For more information about all the features available in Grid, please refer to the Virtual Dataset documentation.
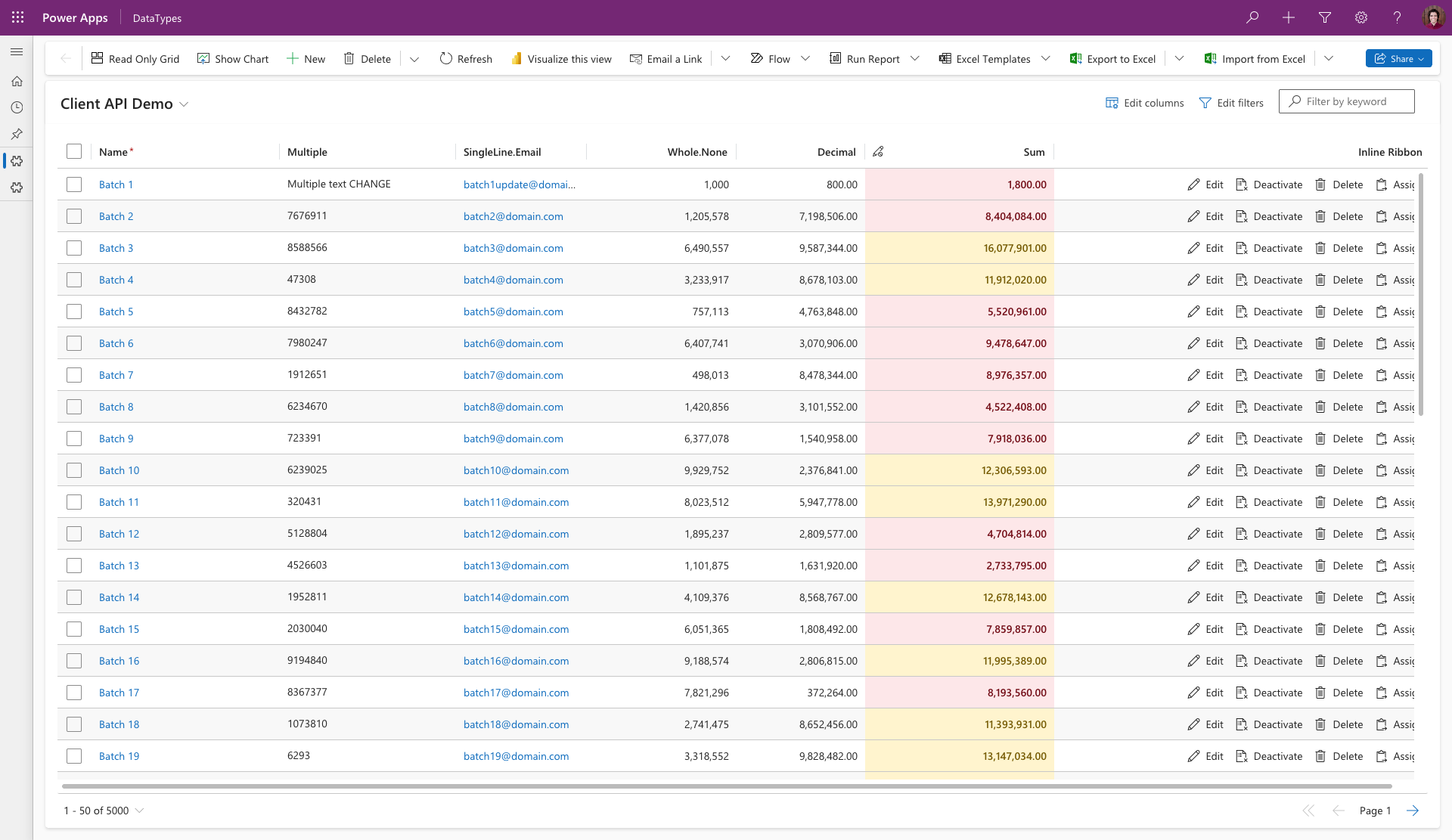 Grid control on Homepage Grid with Client API support.
Grid control on Homepage Grid with Client API support.
# Usage
Since Grid can be directly bound to a Subgrid or Homepage grid, it does not require any additional configuration. You can simply add the Grid control to your form and bind it to the desired dataset. Of course, you can still use other parameters to customize the control's behavior the same way as you would with the Virtual Dataset control. Grid behaves the same as Virtual Dataset with FetchXmlDataProvider, so the behavior (for example in regards to the Columns binding) is identical.
# Column Configuration
When Grid is bound to a Subgrid, column definitions are derived from the underlying Dataverse view. You can override or extend these columns by configuring the Columns parameter on the control. The Columns parameter accepts a JSON array of column definitions — see the Column Configuration section of the Virtual Dataset documentation for a full reference of supported properties.
If the underlying view includes columns from related entities (via link-entity), you must use the dotted notation ({link-entity-alias}.{attribute-name}) in both the name and alias fields. See Related (Linked Entity) Columns for details and examples.
# Ribbon
Grid is able to leverage the same Ribbon commands as the standard Power Apps grids. This means that you can use the existing Ribbon buttons and commands to perform actions on the Grid control, such as creating new records, deleting records, or exporting data. You can also render these buttons inline by following the instructions in the Ribbon section of the Virtual Dataset documentation.
# Grouping
To enable ribbon functionality with grouped records, configure the RibbonGroupingDataset binding to reference a view targeting the same entity as the main dataset. The view must exclude all filters and include any linked entities referenced in the main dataset.

