Security Role
# Security Role
A security role defines how different users access different types of records.
There are bunch of security roles predefined by Microsoft but we usually cannot use them since our solutions are highly customized.
There is actually really nice and clear documentation about security roles from MS so on this page is mostly about useful tips.
MS Docs: Security Roles Documentation (opens new window)
# General
# Access levels in short
MS Docs: "Access levels determine how deep or high in the organizational business unit hierarchy the user can perform the specified privilege."
Access levels define how much an user can see with business unit and security roles assigned. In short: A security role defines how you can interact with records and business unit defines region of records. See Business Unit description bellow.
Simplified Access level overview from MS Docs:
| Access level | Scope | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Global | Organization | User has access to all records. |
| Deep | Parent: Child Business Units | User has access to every record in his business unit and child business units. |
| Local | Business Unit | User has access to every records in his business unit. |
| Basic | User | User has access only to records he owns. |
| None | _ | User does not have access to any records. |
# Business Unit
MS DOCS: "A business unit is a logical grouping of related business activities."
Business Unit is used when you need to create a hierarchy in your organization. It means that you are able to improve security by filtering what can users interact with.
MS Docs: Business Units Documentation (opens new window)
Useful info:
- There is always one main business unit for an environment.
- You cannot remove main business unit.
- Hierarchy is made by filling Parent Unit lookup field.
- A "Business Unit Team" is generated for every business unit and users with assigned business unit are automatically part of that team.
# Model Example
Let´s make it as simplest as possible. This example is extremely shortened, security roles are way more complex. Be careful while editing them.
Task: Hierarchy for read permission for Orders entity.
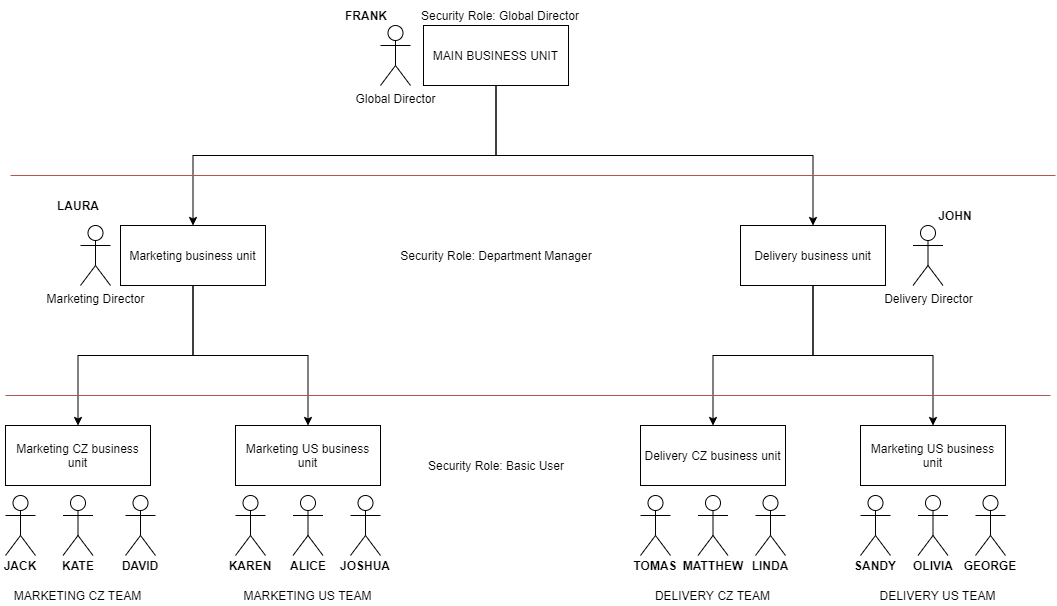
Requirements:
- Global manager has to see all orders.
- Department manager has to see all orders that he owns or his subordinades do.
- Team member has to see all orders which he is owner of or owner is some other member of the team he is in.
There are 3 security roles:
- Global Director
- Departmant Director
- Basic User
Table of assigned Access Levels to Read permisson for Orders entity for these security roles:
| Security Role | Access Level | Users with this role |
|---|---|---|
| Global Director | Global | FRANK |
| Departmant Director | Deep | LAURA, JOHN |
| Basic User | Local | Everyone else |
Who can set what?
Imagine that every user is owner of exactly one record of entity Order. This table which visualize who can see whos records:
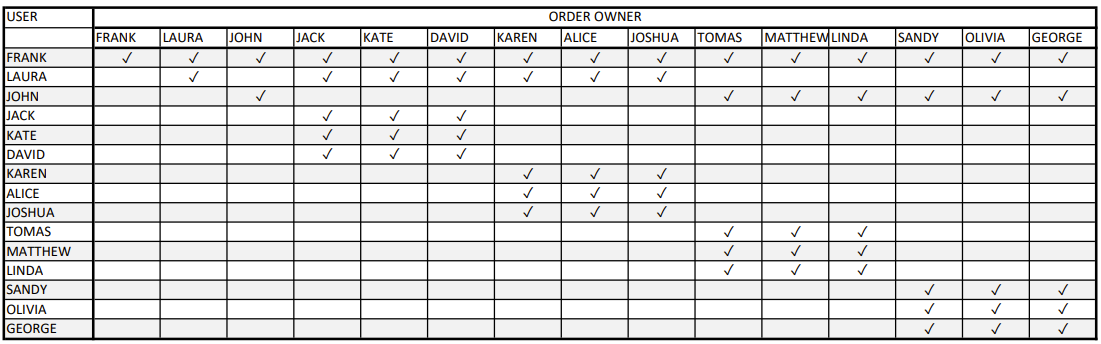
# Tips & Tricks
This set of information might help you with assigning security roles and troubleshooting issues.
# Security Role Update
It was possible to update security roles with solution layering. You could have a security role defined in a main solution and customize it afterwards in extensive solution.
Unfortunately after a MS update this is no longer possible. Solution layers do not apply on security roles anymore.
You have basically two options:
- Update security role in original solution.
- Create a new one in extensive solution.
# Multiple Roles Assigned
Security role priviledges are cumulative which means that user have highest access level from all assigned security roles.
Example:
User XY has two security roles assigned, "Basic User" and "Power User".
Basic User security role has besides others Write priviledge on entity Contact on Access Level = Local. Which means that he can edit all records from same business unit.
Power User security role has besides others Write priviledge on entity Contact on Access Level = Global. Which means that he can edit all records in the system.
The outcome is that this user can edit all records in system.
# Bulk assign
Native securite roles assigned to a business unit team are assigned to all users in that team automatically.
Custom security roles do not behave like that. You have to go one by one and assign security roles for every user.

