TALXIS Async Jobs
# Asynchronous Jobs
TALXIS Async Jobs is an environment independent way to easily trigger and handle asynchronous logic. There are two main components
# Entities
Entity diagram:
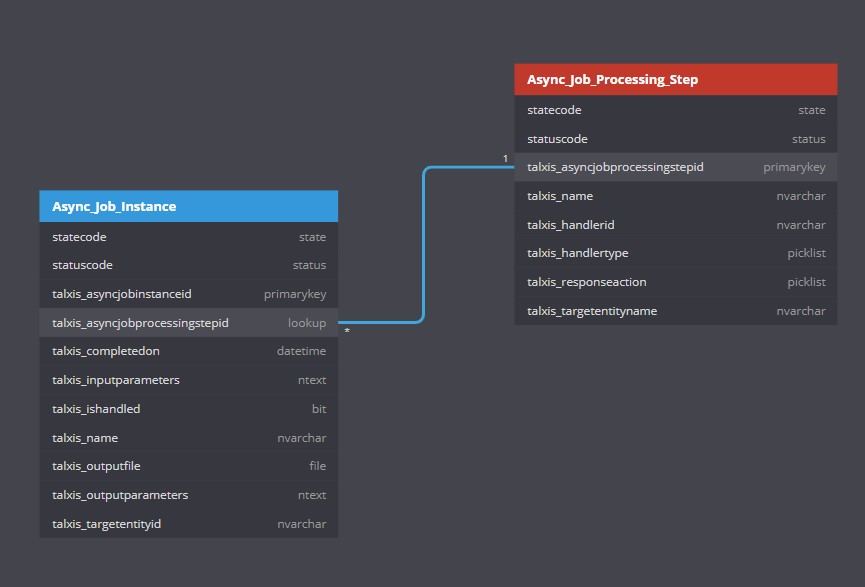
# Async Job Instance
| Field name | Description |
|---|---|
| talxis_asyncjobinstanceid | ID of the record |
| talxis_asyncjobprocessingstepid | ID of the parent Processing Step |
| State Code | Active/Inactive |
| Status code | Queued, Running, Successful, Failed - Update this manualy in your logic to keep track of the async job progress. |
| talxis_targetentityid | ID of the record connected to this instance. Leave blank for subgrids. |
| talxis_name | Name of the instance (Action sets this to be the same as the processing step) |
| talxis_ishandled | True/False - Is used to determine if the user has already seen the "Job complete" dialog, so that it doesn't pop up again. |
| talxis_completedon | Time of completition of the job. Update this manualy in your logic - it is a required field. |
| talxis_inputparameters | Empty text field - If your logic needs any input parameters, add them here |
| talxis_outputparameters | Empty text field - If your logic returns any parameters you need later, add them here |
| talxis_outputfile | File field - If your logic generates a file, save it to this field. The user will have the option to download this from the browser |
# Async Job Processing Step
| Field name | Description |
|---|---|
| talxis_asyncjobprocessingstepid | ID of the Processing Step |
| talxis_name | Name of the processing step |
| talxis_targetentityname | Logical name of the entity connected to this processing step |
| talxis_handlerid | An arbitrary id of this processing step, used to track in your logic (NOT USED CURRENTLY) |
| talxis_handlertype | Flow/Http - The way this processing step is handled asynchronously (NOT USED CURRENTLY) |
| talxis_responseaction | Redirect,Download,Notify,DownloadExternal - Action to be performed by browser after the async job finishes |
| talxis_runningnotificationmessage | Running notification message - use custom message for running notification. GetLocalizedString function is automatically called when the running message is displayed, so you can use resource files for localization of this string. Use format described here if you wish to use resource file. |
| talxis_confirmdialogtitle | Custom title of the confirm dialog. GetLocalizedString function is automatically called when the confirmation dialog is displayed, so you can use resource files for localization of this string. Use format described here if you wish to use resource file. |
| talxis_confirmdialogsubtitle | Custom subtitle of the confirm dialog. GetLocalizedString function is automatically called when the confirmation dialog is displayed, so you can use resource files for localization of this string. Use format described here if you wish to use resource file. |
| talxis_confirmdialogtext | Custom text of the confirm dialog. GetLocalizedString function is automatically called when the confirmation dialog is displayed, so you can use resource files for localization of this string. Use format described here if you wish to use resource file. |
| talxis_confirmdialogconfirmbuttonlabel | Custom confirm button label of the confirm dialog. GetLocalizedString function is automatically called when the confirmation dialog is displayed, so you can use resource files for localization of this string. Use format described here if you wish to use resource file. |
| talxis_confirmdialogcancelbuttonlabel | Custom cancel button label of the confirm dialog. GetLocalizedString function is automatically called when the confirmation dialog is displayed, so you can use resource files for localization of this string. Use format described here if you wish to use resource file. |
talxis_responseactions:
- Redirect: After completition, the user will get a pop up about completition and a chance to get redirected. Flow example:
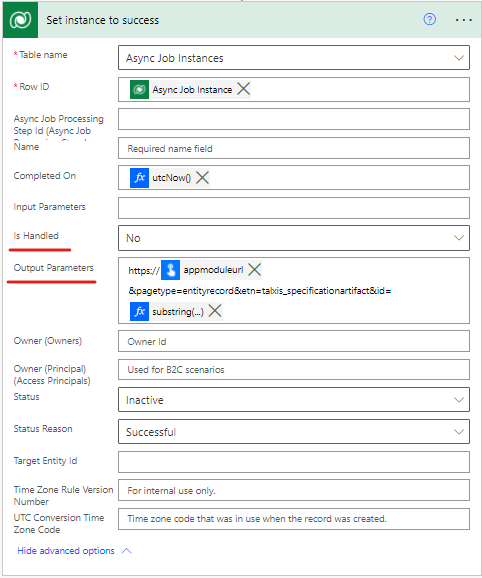
- Download & DownloadExternal: After completition, the user will get a pop up about completition and a chance to download the file. If the action is "Download", the button will download the file from the file field. If the action is "DownloadExternal", the button will try to look into the "output parameters" field for a URL and try to download the file from that. (Example: Powerpoint connector returns a URL to blob storage, where the file is generated.)
- Notify: After completition, the user will get a pop up about completition.
Sample record:
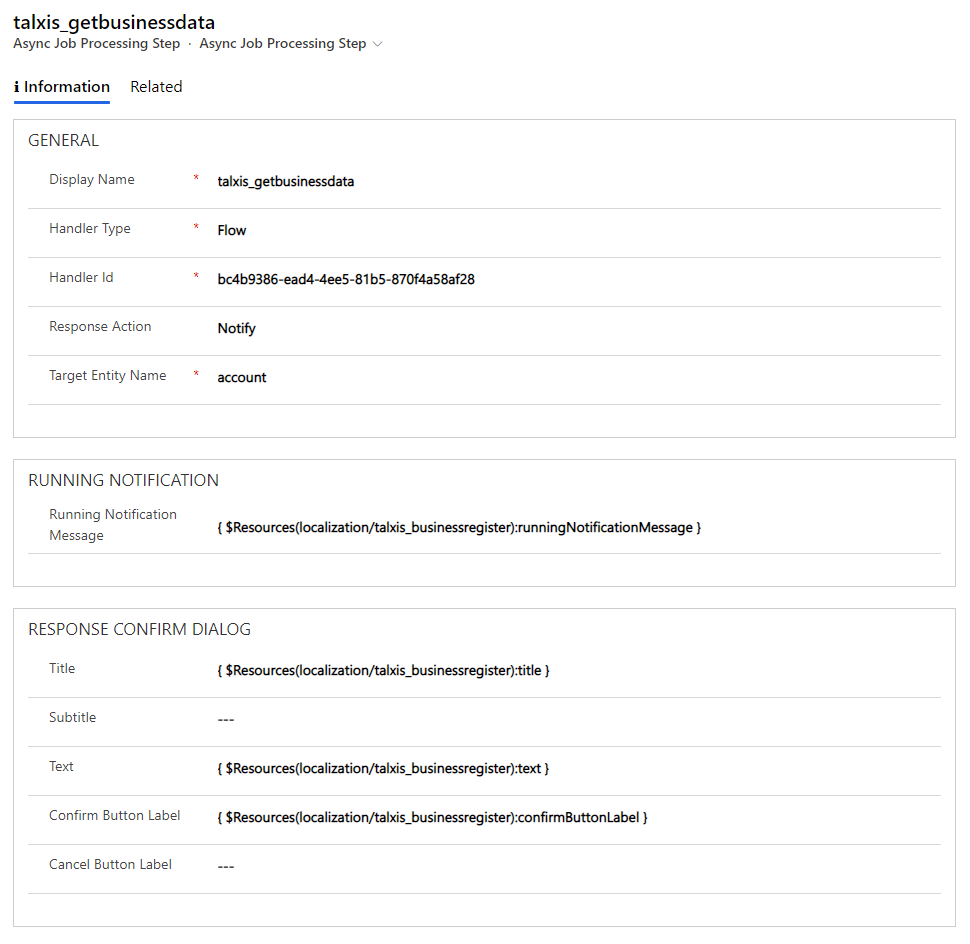
# Workflows/Actions
# talxis_timeoutjob
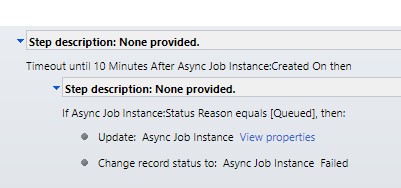
Triggers on create of Async job instance. After 10 minutes of the instance being in the queued state (assuming the logic has not run) cancels the instance as failed.
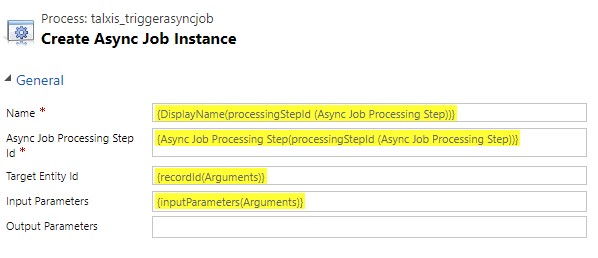
# talxis_triggerasyncjob
Action that takes inputs: processingStepId, recordId. Optional parameter is: inputParameters
- processingStepId is the ID of the processing step record this async job is connected to.
- recordId is the ID of the related record this async job is connected to. The empty GUID
00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000can be used to indicate that the operation is unbound - not related to any record.
This action creates and async job instance based on the parameters. Only step being "Create Async Job Instance"
Example of usage on client can be found here (opens new window)
# Script
# Usage
Basic
talxis_asyncjobs.ts is a big part of this feature. To use the script as a package, include this on the form of the entity you want your instances to run on.
<formLibraries>
<Library name="talxis_asyncjobs.js" libraryUniqueId="{25000CAE-8C42-4CD3-98A4-842DAD73843E}" />
</formLibraries>
<events>
<event name="onload" application="false" active="true">
<Handlers>
<Handler functionName="Talxis.Utility.Features.AsyncJobs.AsyncHandler.Main" libraryName="talxis_asyncjobs.js" handlerUniqueId="{26FB83F0-8521-41A6-A93F-4E01E752C6F5}" enabled="true" parameters="" passExecutionContext="true" />
</Handlers>
</event>
</events>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
The Main function on its own handles
- Rendering the status notification

- Polling running instances to check their status
- Render the pop up on completition of the async instance
- Handle the action (download, redirect etc.)
- Update the instance after it has been handled by the user
Advanced
The script can also be used as a library.
You can use the methods SortInstances and GetAsyncJobs to get an object of relevant async jobs running on the record
class SortedJobs {
QueuedOrActive: any[] = []
Successfull: any[] = []
Failed: any[] = []
}
2
3
4
5
How it works
The Main method first uses
this.SortInstances(await this.GetAsyncJobs(executionContext));
to get all relevant async job instances for the current record. After sorting them into the object, we can go thorugh the different states.
For each successfull notification, we call
ShowDownloadNotificationto raise up the pop up dialog (depending on the AlertType) and after the dialog is handled withHanleOutputwhich then switches between functionsDownloadFile,RedirectandDownloadExternal.For each failed messages, we call
ShowFailedNotificationto open the failed notification.For each running or queued request, we call
ShowRunningNotificationif there is more than one. we also set a timeout to callClearAndRecurseafter 5 seconds
if (refresh) {
setTimeout(() => AsyncHandler.ClearAndRecurse(executionContext, idList), 5000);
}
2
3
After each failed or successfull handling of message, we mark it as handled so that it does not pop up again.
The ClearAndRecurse message deletes all notifications created so far and calls the Main action again, restarting the loop. If there are no pending messages, we don't recurse (meaning that this loop only starts on form load or when explicitely called, from button for example. If some outside factor triggers an async job, we generaly don't catch it until form refresh)
# Example usage in Power Automate flows
Here is a typical usage of async jobs inside of a Flow.
Trigger:
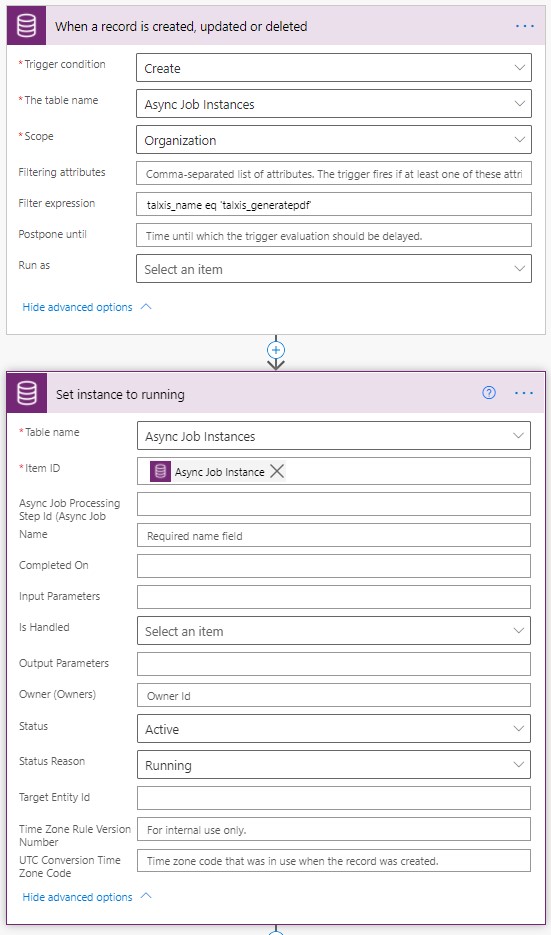
Creating a flow that triggers on create of new Async Job Instances, we can use "Filter Expression" to filter so that it only triggers on the relevant instances. This should be changed in the future so that we trigger on ID and not on name.
Ending:
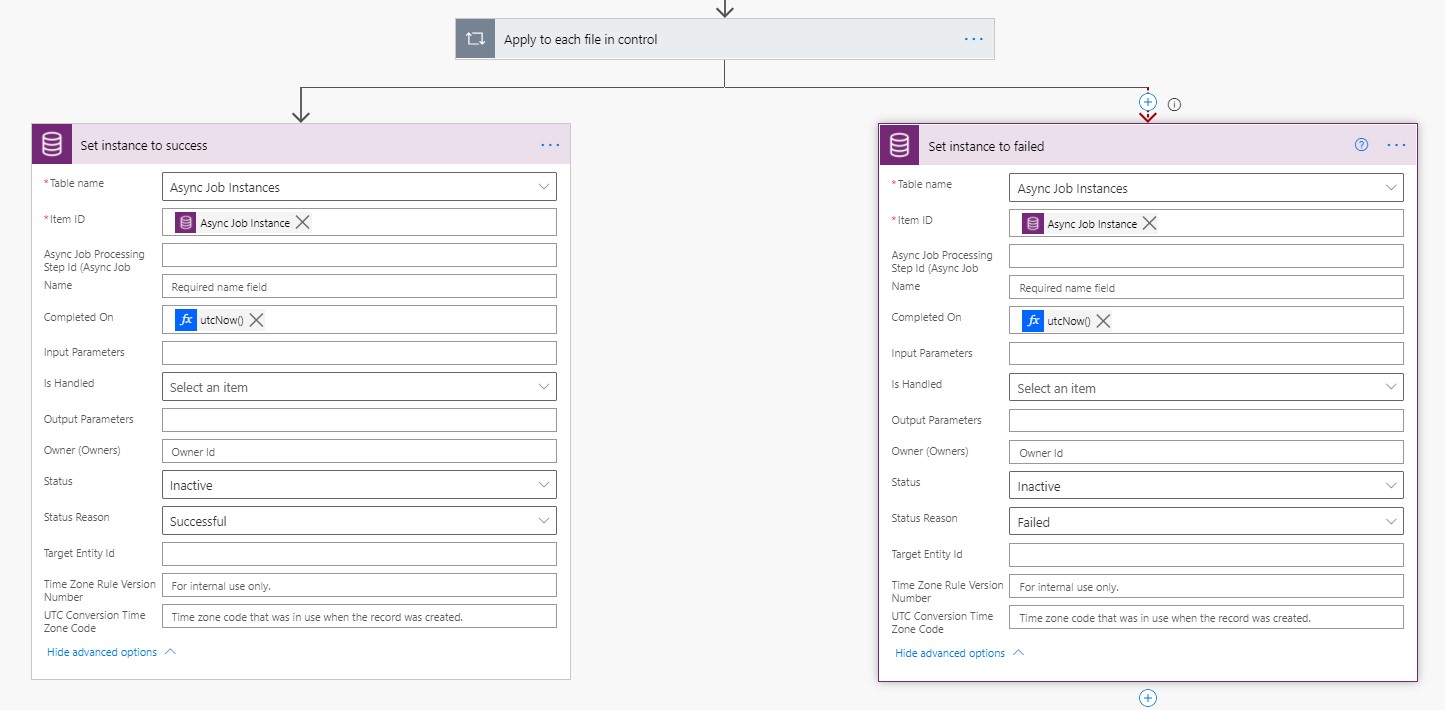
At the end of the flow, we put fork such as this, which sets the status to successful in case everything works and to failed in case any previous step is failed, skipped or has timed out, using run-after.

